Getting Started with Web3: The Power of ethers.js Explained
Introduction
What is Web3 in technical term ?
- Web3 is a term used to describe the next generation of the internet, where decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts are built on blockchain technology.
What is Web3 in simple terms ?
- Web3 is a blend of lots of cryptography , where the data is stored in a immutable chain of blocks.
- You can interact with the deployed chain after deploying your block with help of using the hash of the block.
- In each block we have a hash of the previous block. In each block we can store code, data, and transactions.
Pre-requisites to start with Web3
Curiosity to learn about blockchain technology.
Basic knowledge of JavaScript and Node.js.
You should have a MetaMask wallet installed in your browser.
Let’s get started by making a wallet on MetaMask
- After installing the MetaMask wallet, you will see a fox icon in the top right corner of your browser.
- Click on create a new wallet and set a password for your wallet.
- You will be given a seed phrase which you should keep safe and secure:
- This seed phrase is your actual password to your wallet, so never share it with anyone. This used to convert your private key to public key.
- After setting up your wallet, you will see your wallet address in the top corner of your browser.
Let’s know some basic concepts of Web3
- What is a seed phrase:
- A seed phrase is a list of words that can be used to generate a wallet’s private key with the help of a Mnemonic algorithm.
- What is a private key:
- A private key as the name suggests is a key that should be kept private and secure. It is used to sign transactions and messages in the blockchain. You can understand it as a key to any transaction you make.
- What is a public key:
- A public key is derived from the private key and is used to receive transactions and messages in the blockchain. You can understand it as a key to receive any transaction you make. Your wallet address is the shortened version of your public key.
We use RSA technique to generate the public key and private key. To know more about RSA, you can visit here.
Let’s start with ethers.js
- We discuss previously about the public key and private key. Now we will see how we can interact with the blockchain using these keys.
- We will use the ethers.js library to interact with the Ethereum blockchain.
- Ethers.js makes it easy to interact with the Ethereum blockchain using JavaScript. It is a library that provides a simple and easy-to-use API for interacting with the Ethereum blockchain.
Step 1: Install ethers.js
- You can install ethers.js using npm or yarn in the nodejs. Run the following command in your terminal to install ethers.js:
1
npm install ethers
Step 2: Create a new JavaScript file
- Create a new JavaScript file and import ethers.js at the top of the file (we have made a type: module in the package.json file).:
1
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
Step 3: Connect to the Ethereum blockchain
For connecting to a blockchain, you need to provide a provider. A provider is an object that connects to the Ethereum blockchain and provides access to the blockchain data.
You can connect to the Ethereum blockchain using the Infura provider. Infura is a service that provides access to the Ethereum blockchain without running a full node. Do you full node of actual mainnet blockchain is around 1-2 TB. So it is feasible to use the Infura provider.
You can get your Infura provider by creating an account on the Infura website.
After creating an account on the Infura website, you will get a API Key and a API Secret Key You can use these credentials to connect to the Ethereum blockchain.
You can connect to the Ethereum blockchain using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
// mainnet provider which is used to connect to the mainnet blockchain which uses actual ether.
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://mainnet.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual API Key
// sepolia provider which is used to connect to the sepolia test network which uses test ether.
const sepoliaProvider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual
Do you know What’s the cost of 1 ether in USD 🤔?
- The current price of 1 ether is around $3500 USD.
- Do we need to buy 1 ether to interact with the blockchain ?
- No, you don’t need to buy 1 ether to interact with the blockchain. You can use the test network to interact with the blockchain without spending any real money.
What is the test network ?
- The test network is a network that is used for testing purposes. It is similar to the main Ethereum network but uses fake ether (test ether) that has no real value. You can use the test network to test your smart contracts and dApps without spending real money.
How to get test ether ?
- You can get test ether from the faucet. The faucet is a website that gives you free test ether for testing purposes. You can get test ether by visiting the faucet website and entering your wallet address. The test network I personally use is Sepolia.
- You can get test ether from:
Let’s see how we can interact with the blockchain using ethers.js
We will see how we can get the balance of an Ethereum wallet using ethers.js.
You can get the balance of an Ethereum wallet using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual API Key
const walletAddress = 'YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS'; // Replace YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS with your actual wallet address
const getBalance = async () => {
const balance = await provider.getBalance(walletAddress);
console.log(ethers.utils.formatEther(balance));
};
getBalance();
In the above code, we are using the getBalance method of the provider object to get the balance of the wallet address. We are using the formatEther method of the ethers.utils object to format the balance in ether.
You can run the above code in your terminal to get the balance of your wallet address.
Step 4: Make a new random wallet on ethers.js
- You can create a new random wallet using ethers.js by using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const wallet = ethers.Wallet.createRandom();
console.log(wallet.address);
console.log(wallet.privateKey);
console.log(wallet.mnemonic.phrase);
- In the above code, we are using the createRandom method of the ethers.Wallet object to create a new random wallet. We are logging the wallet address, private key, and mnemonic phrase to the console.
- You can run the above code in your terminal to create a new random wallet.
- You can use the private key and mnemonic phrase to access your wallet in the MetaMask wallet as well.
- The mnemonic phrase is made from 2048 words. You can use any 12 words from the 2048 words to create a new wallet.
Step 5: Sign a message using ethers.js
- You can sign a message using ethers.js by using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const wallet = new ethers.Wallet('YOUR_WALLER_PRIVATE_KEY');
const signMessage = async () => {
const message = 'Hello, Minav!';
const signature = await wallet.signMessage(message);
console.log(signature);
};
signMessage();
- In the above code, we are using the signMessage method of the wallet object to sign a message. We are logging the signature to the console.
- You can run the above code in your terminal to sign a message.
- You can use the signature to verify the message using the public key of the wallet.
- You can also use the signature to sign transactions in the blockchain.
- Signing is a very important concept in the blockchain. It is used to verify the authenticity of the message or transaction.
Step 6: Send ether from one wallet to another wallet
- Here you can see how you can send ether from one wallet to another wallet using ethers.js.
- You can also check your metamask wallet to see the eth increasing and decreasing.
- You can send ether from one wallet to another wallet using ethers.js by using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual API Key
const wallet = new ethers.Wallet('YOUR WALLER PRIVATE KEY', provider);
const sendEther = async () => {
const tx = {
to: 'RECEIVER WALLET ADDRESS',
value: ethers.parseEther('0.1')
};
const sendTx = await wallet.sendTransaction(tx);
console.log(sendTx.hash);
await sendTx.wait();
console.log('Transaction confirmed');
};
sendEther();
- In the above code, we are using the sendTransaction method of the wallet object to send ether from one wallet to another wallet. We are using the parseEther method of the ethers object to convert the ether value to wei.
- One ether is equal to 10^18 wei. So, we are converting 0.1 ether to wei using the parseEther method.
- You can run the above code in your terminal to send ether from one wallet to another wallet.
- You can check your MetaMask wallet to see the ether balance decreasing in the sender wallet and increasing in the receiver wallet.
- You can also check the transaction hash in the search bar to see the transaction details on etherscan.
In the above code,
const wallet = new ethers.Wallet('YOUR WALLER PRIVATE KEY', provider);
is a signer object that is used to sign the transaction before sending it to the blockchain.
What is a signer object?
- A signer object is an object that is used to sign transactions and messages in the blockchain. It is created using the private key of the wallet. Don’t worry during signing the transaction, the private key is not shared with anyone. It is used to sign the transaction and then it is destroyed.
- You can understand it as a key to any transaction you make.
Step 7: Use the ethers.js library to interact with smart contracts
- You can use the ethers.js library to interact with smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
We will discuss how you can interact with smart contracts using ethers.js.
- You can interact with smart contracts using ethers.js by using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual API Key
const wallet = new ethers.Wallet('YOUR_WALLER_PRIVATE_KEY', provider);
const contractAddress = '0x89c12CB862c41736C800460F3488959ECcdd6679';
// Replace CONTRACT_ADDRESS with the actual contract address taken from https://sepolia.etherscan.io/address/0x89c12cb862c41736c800460f3488959eccdd6679
const contractABI = [/ * CONTRACT_ABI * /];
// Replace CONTRACT_ABI with the actual contract ABI taken from https://sepolia.etherscan.io/address/0x89c12cb862c41736c800460f3488959eccdd6679 which is like the docs of API for the contract
// Signer is used for write functions
// Provider is used for read-only functions
const contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, contractABI, SignerOrProvider);
const callContract = async () => {
const result = await contract.someFunction(); // Replace someFunction with the actual function name of the smart contract
console.log(result);
};
callContract();
- In the above code, we are using the Contract object of the ethers.js library to interact with the smart contract. We are using the someFunction method of the contract object to call the function of the smart contract.
- What is a contract ABI?
- The contract ABI is a JSON object that defines the interface of the smart contract. It contains the functions, events, and variables of the smart contract. You can get the contract ABI from the etherscan website.
- It can be said as the API docs of the smart contract.
- You can use my contract address and ABI to interact with the smart contract.
- You can run the above code in your terminal to interact with the smart contract.
- You can check the result of the function call in the console.
- You can also check the transaction hash in the search bar to see the transaction details on etherscan.
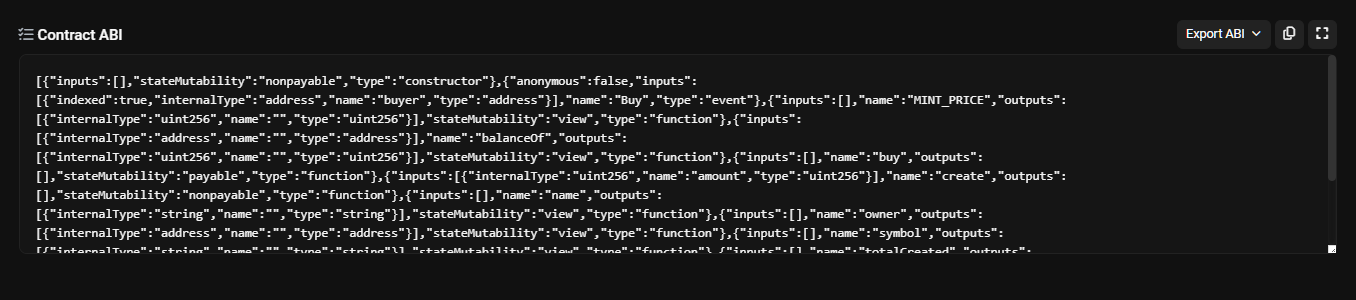 Image of the Contract ABI —
Image of the Contract ABI —
Step 8: Use the ethers.js library to interact with smart contracts with parameters
- You can use the ethers.js library to write functions with smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
- We will discuss how you can write functions with smart contracts using ethers.js.
- You can write functions with smart contracts using ethers.js by using the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY'); // Replace YOUR_INFURA_API_KEY with your actual API Key
const signer = new ethers.Wallet('YOUR_WALLER_PRIVATE_KEY', provider);
const contractAddress = '0x89c12CB862c41736C800460F3488959ECcdd6679';
const contractABI = [/ * CONTRACT_ABI * /];
const functionSelector = "0x110bcd45"; // First 4 bytes of the hash of the function name
const abiCoder = ethers.AbiCoder.defaultAbiCoder();
// Signer is used for write functions
// makeNFT(to, value)
// We get a hash of the function and the parameters concatenated
const encodedData = abiCoder.encode(
["address", "string"],
[address, metaDataHash]
);
const cleanEncodedData = encodedData.startsWith('0x') ? encodedData.slice(2) : encodedData;
const data = `${functionSelector}${cleanEncodedData}`;
const writeContract = async () => {
const tx = await signer.sendTransaction({
to: contractAddress,
data: data
});
console.log(tx.hash);
tx.wait();
console.log('Transaction confirmed');
};
writeContract();
- In the above code, we are using the sendTransaction method of the signer object to write functions with the smart contract. We are using the encode method of the abiCoder object to encode the function parameters.
- You can run the above code in your terminal to write functions with the smart contract.
- You can check the transaction hash in the search bar to see the transaction details on etherscan.
- You can also check the transaction details in the console.
- You can use the functionSelector to get the first 4 bytes of the hash of the function name. You can get the functionSelector from the etherscan website.
- You can use the encodedData to encode the function parameters. You can get the encodedData from the etherscan website.
Conclusion and Giveaway
- In this article, we discussed how you can get started with Web3 using the ethers.js library. We discussed the basic concepts of Web3, how to create a wallet on MetaMask, and how to interact with the Ethereum blockchain using ethers.js.
- We also discussed how to connect to the Ethereum blockchain, create a new random wallet, sign a message, send ether from one wallet to another wallet, and interact with smart contracts using ethers.js.
- We also discussed how to interact with smart contracts with parameters using ethers.js.
- If you have any questions or feedback, please mail me at
minavpkaria@gmail.comor if you are shy to mail me, you can clarify your doubts my prompting to ChatGPT. - I hope this article helps you get started with Web3 and ethers.js. Please feel free to send 0.01 sepolia ETH to the address
0x8f441451B0E30ef063e8FA07F69f2444dD26631Cfor acknowledging my work. - We will discuss more advanced concepts of Web3 in future articles. Stay tuned for more updates!
Happy coding! 🚀 , Stay Curious.